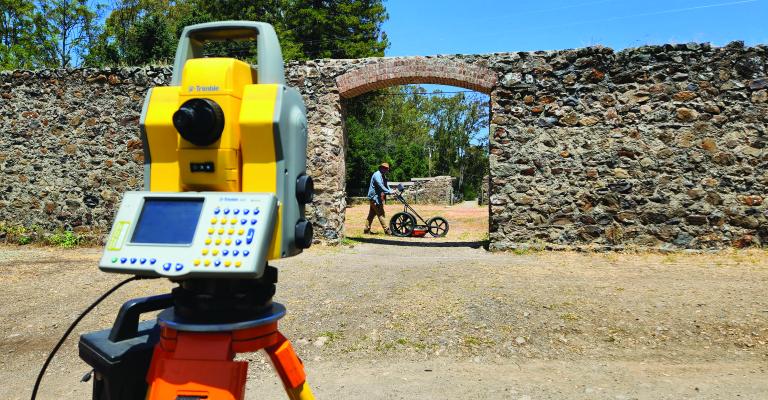
What is CRM Consultation
What is Cultural Resource Management?
Cultural Resource Management involves inventorying sites, evaluating them, and sometimes mitigating the adverse effects of development projects and construction. ASC staff has extensive experience in:
- archaeological survey (inventory)
- recording historic buildings
- consulting with Native American tribes
- evaluating resources according to State of California and Federal standards
- providing advice to landowners and developers to help them comply with CEQA and Section 106 of NHPA
What does Cultural Resource Management mean to home owners?
The following is based on excerpts from “A to Guide to Cultural Resource Management for California Planners, Developers, Contractors, and Property Owners, 1995,” by The Chambers Group, Inc., California.
What are cultural resources?
Cultural resources are the remains and sites associated with human activities and include the following: prehistoric and ethnohistoric Native American archaeological sites; historic archaeological sites; historic buildings; elements or areas of the natural landscape which have traditional cultural significance.
What does the law say about cultural resources?
Federal regulations for cultural resources are governed primarily by Section 106 of the National Historic Preservation Act of 1966. Implementing regulations for the Section 106 review process are found in 36 CFR 800. The goal of this process is to offer a measure of protection to sites which are determined eligible for listing on the National Register of Historic Places. Federal regulations only come into play in the private sector when a project requires a federal permit or if it uses federal money. Federal regulations may also apply if a project comes under the jurisdiction of the California Coastal Commission.
Why do private projects need to consider these regulations?
Most private development projects in California have to consider cultural resources under the California Environmental Quality Act (CEQA) whenever county or city permits are required. In such cases, CEQA mandates that the project's potential environmental effects, including impact upon cultural resources, be reviewed. If the review indicates that no impacts to environmental resources would occur from the proposed project a Negative Declaration is issued and the project may proceed without further consideration. When cultural resources are involved, however, a Negative Declaration cannot be issued without first evaluating the importance of the cultural resources.
Are local governments involved in any way?
A number of cities and counties have passed their own local ordinances regarding cultural resources. Many of these ordinances have specific provisions to protect local cultural resources that are deemed important to the local community or county but which may not be sufficiently protected by state and or federal regulations.
When should a property owner seek outside assistance?
As soon as a project is conceived, and prior to investing money in project design, it is strongly recommended that the developer or landowner go to the appropriate city or county planning department and ask for guidance regarding cultural resources. Should the planner in charge of cultural resources recommend a cultural resource study, the developer or landowner can select a consultant from a list of professional archaeologists and their firms. This list is available from one of the Regional Archaeological Information Centers or the County Planning Department. It is prudent to secure a professional to conduct the necessary research.
What will an archaeologist do if there are cultural resources on my property?
The consulting archaeologist may recommend inventory, evaluation, and/or treatment of important affected cultural resources. Discovering cultural resources on a property does not mean that construction cannot go ahead. It simply means that landowners and/or developers, with the assistance of an archaeologist must pursue the appropriate strategies to protect, record, and/or recover the resources.


